RaceCapturePro Lua Scripting
RaceCapture/Pro Scripting Guide
Example Scripts and How-Tos
A large collection of example scripts can be found in our Lua Scripting Examples
Lua Script Basics
Conventions
- All inputs and outputs are numbered starting at 0 (getGpio(0), setChannel(0), etc)
- All channel values must be numbers
- All virtual channel names must have no spaces (to be fixed in future revisions)
Writing your script
onTick() function
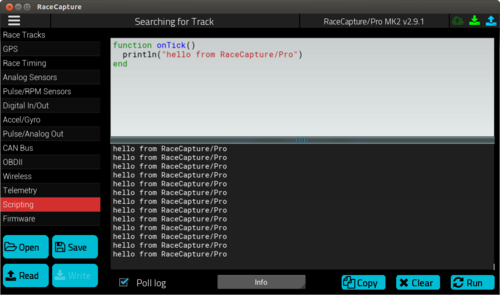
Your Lua script is centered around the onTick() function. RaceCapture/Pro will periodically call this function and here you can define your custom tasks and logic.
Example: this script will periodically write a message to the log:
function onTick()
println("hello from RaceCapture/Pro")
end
Viewing the output log
You can observe the loading of new script and monitor and debug the behavior of your script by using the print() / println() functions. In order to see the log output, enable the "Poll Log" checkbox in the scripting window:
=Controlling the onTick() rate
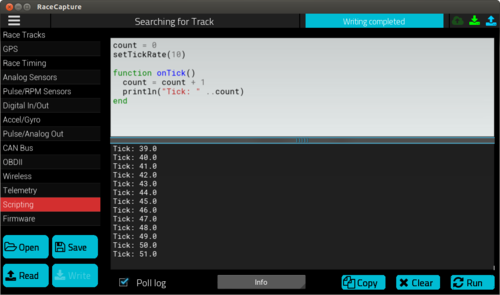
You can control how fast your script is executed using the setTickRate() function. The tick Rate is specified in Hz, and the default rate is 1Hz.
count = 0
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
count = count + 1
println("Tick: " ..count)
end
Reading and controlling inputs and outputs
The Lua scripting enables endless combinations of custom behaviors by reading sensor values, controlling output lines, broadcasting CAN messages and writing data to the Auxiliary serial port.
Example: Reading a sensor value and activating an output based on a threshold.
Given:
- A calibrated temperature sensor is connected to the first analog input (0);
- The first GPIO is configured for output mode
This script will activate the output upon crossing the temperature threshold of 212.
function onTick()
temperature = getAnalog(0)
if temperature > 212 then
setGpio(0, 1)
else
setGpio(0, 0)
end
end
Combining multiple functions
When combining multiple functions into one script, it's recommended to break them into multiple functions and reference them from the main onTick() function.
Example:
function checkTemps() [ temperature checking logic goes here ] end function checkAutoLogging() [ automatic logging logic goes here ] end function onTick() checkTemps() checkAutoLogging() end
More examples
You can see more examples in our Lua Scripting Examples section.
API Reference
General Input / Output (GPIO) Functions
getGpio( channel )
Retrieves the state of the specified GPIO channel
- params
- channel: integer 0 - 2
- returns:
- state: 1 = channel is high, 0 = channel is low
When the channel is configured for input mode, a voltage high input (> 2 volts) will read as 1; a voltage low will read as 0. A disconnected channel will read as high due to the internal pullup resistor.
When the channel is configured as output, the channel reads 1 when the channel is activated (output transistor is connected to ground) and 0 when the channel is deactivated (pullup resistor is active)
setGpio ( channel, state )
Sets the state of the GPIO channel when the channel is configured for output mode.
- params
- channel: integer 0 - 2, state - 1 = output active; 0 = output inactive
- returns:
- none
When the state specified is 1, the output is active (transistor is connected to ground). When state is 0, transistor is disconnected, and pullup resistor is active.
When configured for input mode this function has no effect.
getButton()
Gets the state of the front panel pushbutton.
- params
- none
- returns
- state: 1 = pushbutton is depressed; 0 = pushbutton is not depressed
PWM / Analog Output functions
setPwmDutyCycle( channel, dutyCyclePct )
Sets the duty cycle of the specified PWM / Analog output channel to the specified duty cycle percentage
- params
- channel: PWM / Analog output channel 0 - 3
- dutyCyclePct: Percentage value of the duty cycle as a counting number 0 - 100
- returns
- none
setPwmClockFreq( frequency )
Sets the clock frequency of the PWM outputs
- params
- frequency: the frequency of the PWM clock, in Hz. Supported range is 320-40000 Hz
- returns
- none
setAnalogOut( channel, voltage )
Sets the output voltage of the specified PWM / Analog output channel to the specified period. A convenience function equivalent to setPwmDutyCycle that translates voltage to PWM percentage.
- params
- channel: PWM / Analog output channel 0 - 3
- voltage: the specified output voltage ( 0 - 5v)
- returns
- none
Timer / RPM Sensor Functions
getTimerRpm(channel)
Returns the current RPM of the specified timer input channel. Note, the timer channel configuration must be set to RPM mode.
- params
- channel: Timer channel 0 - 2
- returns: RPM value
getTimerPeriodMs(channel)
Returns the current duration of the full cycle pulse of the specified timer input channel, in milliseconds. Note the timer channel configuration must be set to Duration mode.
- params
- channel: Timer channel 0 - 3
- returns: millisecond value
getTimerFreq(channel)
Returns the current frequency present on the specified timer input channel, in Hz. Note the timer channel configuration must be set to Frequency Mode.
- params
- channel: Timer channel 0 - 3
- returns: Frequency in Hz
getTimerRaw(channel)
Returns the current raw timer value as measured on the specified timer input channel.
- params
- channel: Timer channel 0 - 3
- returns: Raw timer value between 0 - 65535
Analog Sensor Functions
getAnalog(channel)
Reads the scaled analog value for the specified analog input channel.
- params
- channel: Analog input channel 0 - 7
- Note: channel 7 is internally dedicated to battery voltage.
- returns: Scaled / calculated value for the specified analog channel as defined in the channel scaling configuration
- channel: Analog input channel 0 - 7
Accelerometer / Yaw Sensor Functions
getImu(channel)
Reads the specified IMU channel
- params
- channel (0 - 2 for accelerometer, 3 for yaw gyro sensor)
- returns
- The value scaled to G force, or degrees/sec depending on the channel selected
getImuRaw(channel)
Reads the raw value of the specified accelerometer or yaw channel
- params
- channel (0 - 2 for accelerometer, 3 for yaw gyro sensor)
- returns
- The raw accelerometer value
GPS Sensor Functions
getGpsPos()
Reads the current position as measured by the attached GPS module coming in firmware 2.0
- params
- none
- returns
- Latitude: latitude in decimal degrees
- Longitude: longitude in decimal degress
getGpsSpeed()
Provides the current speed as measured by the attached GPS module
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The current speed in MPH
getGpsQuality()
Provides the current GPS quality indicator as indicated by the attached GPS module
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The current GPS quality indicator
- 0: No fix; 1: Fixed; 2: SPS Fix; 3: Differential Fix
getGpsTime()
Provides the current GPS time as indicated by the attached GPS module (in NMEA format) todo: document this
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The current GPS time value
getGpsDist()
Provides the current GPS calculated distance from the beginning of the logging session, or from the start finish line, if configured.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The distance, in Miles
getGpsAltitude()
Provides the current GPS calculated altitude from sea level in feet. The method will return 0 if there is no GPS lock.
- Added: v2.9.0
- Parameters: None
- Returns: <altitude>
getLapCount()
Provides the current Lap Count as determined by the start/finish line configuration and measured by the attached GPS module.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The number of laps detected since the logging session started
getLapTime()
Provides the last lap time as determined by the start/finish line configuration and measured by the attached GPS module.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- The last measured lap time in decimal minutes / seconds
getGpsSec()
Provides the number of seconds since midnight, as measured by the GPS module. todo: how does this relate to timezone? GMT or local?
- params
- (none)
- returns
- number of seconds since midnight, as measured by the attached GPS module
getAtStartFinish()
Indicates if within the start finish line target as determined by the start/finish line configuration and measured by the attached GPS module.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- 1 if currently within the start/finish line target, 0 if outside
getTimeDiff(time1, time2)
Utility function to calculate the absolute difference between two time values, in seconds. todo: investigate the need for this function. may be eliminated in 1.2 firmware
- params
- time1
- time2
- returns
- The absolute difference between the specified values
getTimeSince(time)
Utility function to calculate the time since midnight, in seconds. todo: investigate the need for this function. may be eliminated in 1.2 firmware
- params
- time
- returns
- The number of seconds since midnight
CAN Bus functions
initCAN(channel, baud )
available in firmware 2.0 Initializes the CAN bus module. Normally this is done when RaceCapture/Pro powers on; use this function if you need to change the CAN baud rate on the fly.
- params
- channel: The CAN channel. 0 for the first channel, 1 for the 2nd, if supported on the hardware
- baud rate: Supported baud rates: 100000, 125000, 250000, 500000, 1000000
- returns
- 1 if successful, 0 if initialization fails, nil if parameters are incorrect
txCAN(channel, id, isExtended, data, [timeout] )
available in firmware 2.0 Transmit a CAN message.
- params
- channel: The CAN channel. 0 for the first channel, 1 for the 2nd, if supported on the hardware
- identifier: The Identifier value of the message, either in standard (11 bit) or extended (29 bit) format.
- isExtended: 0 for Standard (11 bit) Identifier or 1 for Extended (29 bit) Identifier.
- data: CAN message payload; array up to 8 elements long.
- timeout: (optional) specify a timeout for sending this message. if the transmit queue is full, will block for the specified milliseconds. Defaults to 100ms
- returns
- 1 if successful, 0 if failed, nil if parameters are incorrect
Example:
channel = 0
id = 1234
ext = 0
data = {11,22,33}
res = txCAN(channel, id, ext, data)
rxCAN(channel, [timeout] )
available in firmware 2.0 Receive a CAN message, if available.
- params
- channel: The CAN channel. 0 for the first channel, 1 for the 2nd, if supported on the hardware
- timeout (optional). read timeout in milliseconds. defaults to 100ms. For non-blocking functionality specify a timeout of 0.
- returns
- identifier: The Identifier value of the message, either in standard (11 bit) or extended (29 bit) format.
- isExtended: 0 for Standard (11 bit) Identifier or 1 for Extended (29 bit) Identifier.
- Data: CAN message payload; array up to 8 elements long.
If no CAN message was received, the function returns nil
Example:
id, ext, data = rxCAN(0, 100) --100ms timeout
if id ~= nil then
println("CAN rx: " ..id .." " ..data[1]) --print ID and first element of received message
end
setCANfilter(channel, filterId, extended, filter, mask )
available in firmware 2.0 Sets the specified CAN filter ID, to ignore messages with a particular address. Must use in combination with setCANMask() to set a complete filter and mask.
- params
- channel: The CAN channel. 0 for the first channel, 1 for the 2nd, if supported on the hardware
- filterId: The id of the filter. Up to 6 filters are supported on MK1, 15 per channel on MK2. Filter ids start at 0.
- extended: 0 for Standard (11 bit) Identifier or 1 for Extended (29 bit) Identifier.
- filter: Pattern value for CAN filter
- mask: the mask for the CAN filter
- returns
- 1 for success, 0 for fail, nil if parameters are incorrect
readOBD2( PID )
available in firmware 2.0 Reads an OBD2 PID and returns the calculated value. This is a convenience method wrapped around the built-in CAN functions.
- params
- The OBD2 PID to read. Supported PIDs (TBD documented)
- returns
- The calculated PID value, or nil if the OBD2 PID was invalid or could not be read (e.g. CAN receive message timeout)
Logger Control Functions
onTick()
- params:
- (none)
- returns:
- (none)
The onTick() function is the main loop where scripting activity takes place. By default it is called by RaceCapture/Pro every 1 second (1Hz). The rate can be adjusted using the setTickRate() function.
- Note - you should only define one onTick() function in your code. If multiple onTick() functions are defined, only the last defined onTick() function will be used.
Example:
function onTick()
println("Hello") --write something to the log
end
setTickRate(rate)
Sets the rate at which the onTick() function is called
- params
- rate: The rate the onTick() function is called, in Hz. Max tick rate is 30Hz.
- returns
- (none)
startLogging()
Begins a logging session
- params
- (none)
- returns
- (none)
stopLogging()
Stops the current logging session. If not logging, this function has no effect.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- (none)
setLed( led, state )
Sets the state of a front panel LED
- params
- led (1-3)
- state : 1 = on, 0 = off
- returns
- (none)
setBgStream( on/off )
Sets the state of background streaming
- params
- Boolean: true for on, false for off.
- returns
- (none)
getBgStream()
Gets the state of background streaming
- params
- (none)
- returns
- Boolean: True for on, false for off.
Serial Port Communications
These function calls allow reading / writing line oriented data from the built in serial ports.
Port mappings
0 = USB port
1 = GPS port
2 = Internal telemetry port (MK2 only)
3 = Wireless / Bluetooth port
4 = Auxiliary port
- Note: We only recommend using ports 3 and 4 for connecting script to external devices. Ports 0 - 2 have been included for reference; using them may interfere with normal operations of the unit.
initSer( port, baud, bits, parity, stopBits)
Initializes the specified serial port
- params
- port: The port to initialize. (defaults to Auxiliary port)
- baud: The baud rate to set (defaults to 115200)
- bits: Number of bit in the message (8 or 7) (defaults to 8)
- parity: (1 = Even Parity, 2 = Odd Parity, 0 = No Parity) (defaults to No Parity)
- stopBits: number of stop bits (1 or 2) (defaults to 1)
- returns
- 1 if initialization succeeds, -1 if parameters are incorrect
readCSer( port, [timeout])
Available since firmware 2.8.4
Read a character from the specified serial port
- params
- port: The port to read. (required)
- timeout - the read timeout, in ms.
- returns
- the character read, or nil if the timeout was reached
readSer( port, [timeout])
Read a line of data from the specified serial port. This command blocks until a newline ('\n') character is received on the port, or a timeout occurs.
- params
- port: Serial port 0 - 4
- timeout - the read timeout, in ms.
- returns: a line of serial data, or nil if the timeout was reached
writeCSer( port, data )
Available since firmware 2.8.4
Writes the specified character to the serial port. The call will block until the character is written.
- params:
- port - the serial port to write
- char - the character to write.
- returns:
(no return values)
writeSer( port, data )
Writes a line of data to the specified serial port, appending a newline at the end. The call will block until all characters are written.
- params
- port: Serial port 0 - 4
- data: the data in string format
- returns:
(no return values)
Logger Configuration Functions
flashLoggerCfg()
Writes the current configuration in RAM to flash memory.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- (none)
setPwmClockFreq( freq )
Sets the clock frequency for all PWM channels
- params
- freq: The clock frequency todo: what units?
- returns
- (none)
getPwmClockFreq()
Gets the PWM clock frequency controlling all PWM channels
- params
- (none)
- returns
- the PWM clock frequency todo: what units?
calibrateImuZero()
Automatically Calibrates the accelerometer zero position.
- params
- (none)
- returns
- (none)
Virtual Channels
addChannel( name, sampleRate, [precision], [min], [max], [units] )
available in firmware 2.0 Adds a virtual channel. This virtual channel remains in memory during runtime; it is not persisted in the configuration. Up to 30 virtual channels can be created.
- params
- name: The name of the channel, up to 10 characters long. We recommend using an existing System channel name as defined by the app when possible.
- sampleRate: A supported sample rate (1,10,25,50,100,200Hz)
- precision: (optional) the numerical precision (number of decimal places) used when logging to SD and telemetry. Defaults to 2
- min: (optional) The min expected value for this channel. Defaults to 0
- max: (optional) The max expected value for this channel. Defaults to 1000
- units: (optional) The units label for this channel. Defaults to empty string / none
- returns
- the id of the new virtual channel, or NIL if the virtual channel could not be created. Use this id for setting the channel value (see setChannel() )
getChannel( <Channel ID | Channel Name> )
- Available: v2.9.0
- Parameters
- Channel ID (number) - The channel id value as provided by the addChannel method.
- Channel Name (string) - The name of the channel as provided to the addChannel method. Using the Channel ID method is preferred and is faster.
- Returns
- (number) The value of the channel.
- Examples:
val = getChannel(1)val = getChannel("foo")
setChannel( channelId, value )
available in firmware 2.0 Updates the value of a previously created virtual channel.
- params
- channelId: the ID of the channel provided by addChannel()
- value: the new value to set for the virtual channel
Example:
id = addChannel("EGT", 1)
function onTick()
temp = getAnalog(0) --read analog channel 0
temp = temp * 1000
setChannel(id, temp) --sets the virtual channel value
end
Time Info
These methods get you information about dates and time. This is useful in controlling script behavior or just knowing what time it is.
getUptime()
Available since firmware 2.8.4
Returns the number of miliseconds since the device last started. This is always available and is the most consistent way to time things in LUA script on RaceCapture.
- Returns
- Number of milliseconds since CPU boot.
getDateTime()
Available since firmware 2.8.4
Returns date and time info to the best of the systems ability. Only available after GPS lock has been established. Will return epoch time (Jan 1, 1970 00:00:000) if time is not available.
- Returns: A list of date and time information in the following order:
- Year
- Month
- Day
- Hour
- Second
- Millisecond