RaceCapturePro Lua Scripting Examples: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
sendCheckDTC() | sendCheckDTC() | ||
checkDTCResponse() | checkDTCResponse() | ||
end | |||
</pre> | |||
==Display OBDII Codes as a channel and allow driver to reset the OBDII Codes with a button== | |||
This script creates a virtual channel called OBDIICodes and sets it to the first OBDII Code found (It will not have the alpha prefix (Ie P, C , B, or U), but will just have up to 4 digits. You can then use these digits to figure out the P code. Ie, if 155 is returned, your OBDII code would be P0155. If -1 is shown for the OBDIICodes channel that means RaceCapture has not received any cods from the ECU yet. If 0 is shown for OBDIICodes channel that means the ECU sent back P0000 which means there are no OBDII codes in the ECU. This channel will be logged and sent via telemetry just like a regular channel. | |||
I also added the ability for the driver to reset the OBDII codes using an external button. This button needs to be mapped to an Analog or GPIO channel called ClearOBD. It will reset the vehicles OBDII codes and reset the OBDIICodes channel to -1. | |||
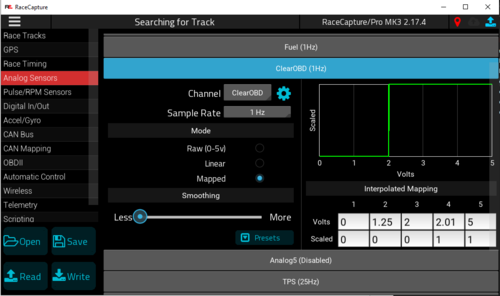
[[Image:ClearOBDChannel.png|500px]] | |||
<pre> | |||
--Modified by Scott Barton of ProFormance Coaching for Autosport Labs Community | |||
setTickRate(10) | |||
--P=Powertrain, C=Chassis, B=Body, U=Network | |||
prefixes = {'P','C','B','U'} | |||
digits = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F'} | |||
addChannel("OBDIICodes", 1, 0) | |||
setChannel("OBDIICodes", -1)-- Some car manufactures send P0000 if there are no fault codes; therefore we will use -1 to know that no codes have been returned yet | |||
function checkClearCodes(canChan) | |||
local ClrOBD = getChannel("ClearOBD") --Must create an analog or GPIO channel called ClearOBD in your settings and map it to read 1 or higher when you push the external button wired to that input | |||
if ClrOBD ~= nil and ClrOBD > 0 then | |||
println('Clearing OBDII codes') | |||
txCAN(canChan, 0x7df, 0, {1,4}) | |||
setChannel("OBDIICodes", -1) | |||
end | |||
end | |||
function toDigit(v) | |||
return digits[v+1] | |||
end | |||
function printDTC(data) | |||
local dtc | |||
local a = data[3] | |||
local b = data[4] | |||
local prefix = prefixes[bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 6), 0x03) + 1] | |||
local c2 = bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 4), 0x03) | |||
local c3 = bit.band(a, 0x0f) | |||
local c4 = bit.band(bit.rshift(b, 4), 0x0F) | |||
local c5 = bit.band(b, 0x0F) | |||
local code = toDigit(c2) ..toDigit(c3) ..toDigit(c4) ..toDigit(c5) | |||
setChannel("OBDIICodes", code) | |||
code = prefix ..code | |||
println('Found DTC: ' ..code) | |||
end | |||
function printRawDTC(data) | |||
print('Raw DTC bytes: ') | |||
--print the remaining 6 bytes, | |||
--this raw data holds the trouble codes | |||
for i=1, #data do print(' ' ..data[i]) end | |||
println('') | |||
end | |||
function checkDTCResponse(canChan) | |||
local attempts = 0 | |||
while attempts < 50 do | |||
local id,ext, data = rxCAN(canChan, 10) | |||
if id ~= nil and ext == 0 and id == 0x7e8 then | |||
if data[2] == 0x43 then | |||
if data[1] > 2 then | |||
printRawDTC(data) | |||
printDTC(data) | |||
else | |||
println('No DTC Found') | |||
end | |||
return | |||
end | |||
end | |||
attempts = attempts + 1 | |||
end | |||
end | |||
function sendCheckDTC(canChan) | |||
println('Sending check DTC') | |||
txCAN(canChan, 0x7df, 0, {1,3}) | |||
end | |||
function onTick() | |||
sendCheckDTC(1) --0=OBDII is on CAN Channel 1; 1=OBD is on CAN Channel 2 | |||
checkDTCResponse(1) | |||
checkClearCodes(1) | |||
end | end | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 21:57, 30 October 2019
How to set a script in the RaceCapture app
HowTo video: set custom script
API Reference
OBDII tricks
Clear current trouble codes
This script clears any current trouble codes every 10 seconds. Clearing the code requires transmitting an OBDII command to ID 0x7DF with mode 4 specified. No other parameters are specified.
setTickRate(1)
count = 0
function onTick()
checkClearCodes()
end
function checkClearCodes()
if count % 10 == 0 then
print('clearing codes')
txCAN(0, 0x7df, 0, {1,4})
end
end
Query and Decode Diagnostic Trouble Code
This script queries for a DTC, and if found, prints the decoded trouble code and the raw data.
--This example queries for and reads the first available DTC, if present.
setTickRate(1)
--P=Powertrain, C=Chassis, B=Body, U=Network
prefixes = {'P','C','B','U'}
digits = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F'}
function toDigit(v)
return digits[v+1]
end
function printDTC(data)
local dtc
local a = data[3]
local b = data[4]
local prefix = prefixes[bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 6), 0x03) + 1]
local c2 = bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 4), 0x03)
local c3 = bit.band(a, 0x0f)
local c4 = bit.band(bit.rshift(b, 4), 0x0F)
local c5 = bit.band(b, 0x0F)
local code = prefix ..toDigit(c2) ..toDigit(c3) ..toDigit(c4) ..toDigit(c5)
println('Found DTC: ' ..code)
end
function printRawDTC(data)
print('Raw DTC bytes: ')
--print the remaining 6 bytes,
--this raw data holds the trouble codes
for i=1, #data do print(' ' ..data[i]) end
println('')
end
function checkDTCResponse()
local attempts = 0
while attempts < 50 do
local id,ext, data = rxCAN(0, 10)
if id ~= nil and ext == 0 and id == 0x7e8 then
if data[2] == 0x43 then
if data[1] > 2 then
printRawDTC(data)
printDTC(data)
else
println('No DTC Found')
end
return
end
end
attempts = attempts + 1
end
end
function sendCheckDTC()
println('Sending check DTC')
txCAN(0, 0x7df, 0, {1,3})
end
function onTick()
sendCheckDTC()
checkDTCResponse()
end
Display OBDII Codes as a channel and allow driver to reset the OBDII Codes with a button
This script creates a virtual channel called OBDIICodes and sets it to the first OBDII Code found (It will not have the alpha prefix (Ie P, C , B, or U), but will just have up to 4 digits. You can then use these digits to figure out the P code. Ie, if 155 is returned, your OBDII code would be P0155. If -1 is shown for the OBDIICodes channel that means RaceCapture has not received any cods from the ECU yet. If 0 is shown for OBDIICodes channel that means the ECU sent back P0000 which means there are no OBDII codes in the ECU. This channel will be logged and sent via telemetry just like a regular channel.
I also added the ability for the driver to reset the OBDII codes using an external button. This button needs to be mapped to an Analog or GPIO channel called ClearOBD. It will reset the vehicles OBDII codes and reset the OBDIICodes channel to -1.
--Modified by Scott Barton of ProFormance Coaching for Autosport Labs Community
setTickRate(10)
--P=Powertrain, C=Chassis, B=Body, U=Network
prefixes = {'P','C','B','U'}
digits = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F'}
addChannel("OBDIICodes", 1, 0)
setChannel("OBDIICodes", -1)-- Some car manufactures send P0000 if there are no fault codes; therefore we will use -1 to know that no codes have been returned yet
function checkClearCodes(canChan)
local ClrOBD = getChannel("ClearOBD") --Must create an analog or GPIO channel called ClearOBD in your settings and map it to read 1 or higher when you push the external button wired to that input
if ClrOBD ~= nil and ClrOBD > 0 then
println('Clearing OBDII codes')
txCAN(canChan, 0x7df, 0, {1,4})
setChannel("OBDIICodes", -1)
end
end
function toDigit(v)
return digits[v+1]
end
function printDTC(data)
local dtc
local a = data[3]
local b = data[4]
local prefix = prefixes[bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 6), 0x03) + 1]
local c2 = bit.band(bit.rshift(a, 4), 0x03)
local c3 = bit.band(a, 0x0f)
local c4 = bit.band(bit.rshift(b, 4), 0x0F)
local c5 = bit.band(b, 0x0F)
local code = toDigit(c2) ..toDigit(c3) ..toDigit(c4) ..toDigit(c5)
setChannel("OBDIICodes", code)
code = prefix ..code
println('Found DTC: ' ..code)
end
function printRawDTC(data)
print('Raw DTC bytes: ')
--print the remaining 6 bytes,
--this raw data holds the trouble codes
for i=1, #data do print(' ' ..data[i]) end
println('')
end
function checkDTCResponse(canChan)
local attempts = 0
while attempts < 50 do
local id,ext, data = rxCAN(canChan, 10)
if id ~= nil and ext == 0 and id == 0x7e8 then
if data[2] == 0x43 then
if data[1] > 2 then
printRawDTC(data)
printDTC(data)
else
println('No DTC Found')
end
return
end
end
attempts = attempts + 1
end
end
function sendCheckDTC(canChan)
println('Sending check DTC')
txCAN(canChan, 0x7df, 0, {1,3})
end
function onTick()
sendCheckDTC(1) --0=OBDII is on CAN Channel 1; 1=OBD is on CAN Channel 2
checkDTCResponse(1)
checkClearCodes(1)
end
Data filtering
Simple RPM Filter
Got a noisy RPM signal where big spikes show up? This will reject RPM values above a sane threshold.
Important - make sure the RPM channel in the main RaceCapture/Pro config is disabled, since this virtual channel replaces it.
--sample RPM at 10Hz
setTickRate(10)
--set this value to be your sane upper limit
rpmLimit = 10000
--In the RCP config, ensure the timer channels are disabled
--we will create the virtual channel here
rpmId = addChannel( "RPM", 10, 0, 0, rpmLimit)
rpm = 0
function doRPM()
local r = getTimerRpm(0)
if r < rpmLimit then
rpm = r
end
setChannel(rpmId, rpm)
end
function onTick()
doRPM()
end
Automatic logging control
Automatically Start Logging When Powered On
This script will automatically start logging the moment RaceCapture/Pro turns on
- Note, this will create a file with an incorrect timestamp if GPS lock is not established.
- To get a properly time-stamped file, use the GPS speed triggered approach.
function onTick() startLogging() end
Automatically Start Logging based on GPS Speed
This script will automatically start logging to SD card when speed exceeds 10MPH and stop when it falls below.
function onTick()
if getGpsSpeed() > 10 then
startLogging()
else
stopLogging()
end
end
Automatically Start Logging when engine is running
This script will automatically start logging to SD card when battery voltage shows that the engine is running
- When battery voltage is greater than 13 volts, we assume engine is running.
- System battery voltage is tied to the last Analog channel (8) (Note, change this to 7 if RaceCapture/Pro MK2)
function onTick()
if getAnalog(8) > 13 then
startLogging()
else
stopLogging()
end
end
Automatically start Logging upon Launch (AutoX / Rally / Hill Climb)
This script will start Logging when a dash mounted "ARM" switch is activated via an input and G-force exceeds a threshold Given:
- GPIO 0 configured as input and connected to dash mounted "Arm" switch
- Default RaceCapture/Pro mounting orientation (terminal block facing forward, mounted upright)
- G-force launch threshold is -0.1 G
- flipping the ARM switch to 'Off' will stop logging
setTickRate(30)
overRevId = addChannel("OverRev", 10)
function onTick()
local arm = getGpio(0)
local g = getAccel(1)
if arm == 0 then
stopLogging()
end
if arm == 1 and g < 0.1 then
startLogging()
end
end
Virtual Channels (AKA Math Channels)
Averaging a fuel level reading or other sensor
This script calculates a moving average to account for fuel slosh. Assumptions:
- Fuel level is connected to the first analog channel and is calibrated; modify the script to base the reading on other channels as appropriate.
--The real analog channel should be named
--something other than FuelLevel
fuel2Id = addChannel("FuelLevel", 10, 0, 0,100,"%")
--change this to make a bigger averaging window
maxAvg = 600
--600 = 20 seconds averaging at 30Hz tick rate
--do not change
fuelAvg={}
fuel2Index = 1
function updateFuelAvg(value)
local i
if #fuelAvg == 0 then
--initialize averaging table
for i = 1, maxAvg do fuelAvg[i]=0 end
end
fuelAvg[fuel2Index] = value
fuel2Index = fuel2Index + 1
if fuel2Index > maxAvg then fuel2Index = 1 end
local sum = 0
for i = 1, #fuelAvg do
sum = sum + fuelAvg[i]
end
setChannel(fuel2Id, sum / maxAvg)
end
setTickRate(30)
function onTick()
updateFuelAvg(getAnalog(0))
end
Average two sensor values and set to a virtual channel
--10Hz update
setTickRate(10)
--Create channel: "SensorAvg"
--Sample rate: 10Hz
--Logging precision: 2 decimal points
--min/max: 0/5
--Units: "Volts"
avgId = addChannel("SensorAvg", 10, 2, 0, 5, "Volts")
function onTick()
local a1 = getAnalog(0)
local a2 = getAnalog(1)
setChannel(avgId, (a1 + a2) / 2)
end
Gear Calculation
Calculate gear position based on drive train ratios, RPM channel and gear. Requires firmware 2.5.0
Edit the gear ratios to match your vehicle. Assumes Speed is available on "Speed" channel, RPM is available on "RPM" channel.
More details under the calcGear API documentation.
setTickRate(30)
--create gear channel
gearId = addChannel("Gear", 10, 0, 0, 6)
function onTick()
-- calculate gear: tire diameter(cm), final gear ratio, individual gear ratios 1-6
local gear = calcGear(62.7, 3.45, 4.23, 2.52, 1.66, 1.22, 1.0, 0.8)
if gear == nil then gear = 0 end
setChannel(gearId,gear)
end
Also available as a preset
Throttle Position Calculation
Estimate throttle position based on G-Forces. 0-100%
--Developed by Scott Barton of ProFormance Coaching for use by Autosport Labs Community
MaxAccelG = 0.30 -- Look at your logs and see what your max acceleration is in 3rd or 4th gear. Note that full acceleration in 5th will not show 100% throttle.
chThrottle = addChannel("vThrottle", 10, 0, 0, 100,'')
function updatevThrottle()
--AccelG = getChannel(LongAccel) --2.13 Firmware and up
AccelG = getImu(0) --Prior to 2.13 Firmware
TPS = (AccelG/MaxAccelG)*100
if TPS < 0 then TPS = 0 end
TPS = math.abs(TPS)
if TPS > 99 then TPS = 100 end
setChannel(chThrottle, TPS)
end
--10Hz update
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
updatevThrottle()
end
Brake Position Calculation
Estimate brake pedal position based on G-Forces. 0-100%.
--Developed by Scott Barton of ProFormance Coaching for use by Autosport Labs Community
MaxDecelG = 1.20 --Look at your logs and see what your maximum g-forces under straight line braking is and round down.
chBrake = addChannel("vBrake", 10, 0, 0, 100, '')
function updatevBrake()
--BrakeG = getChannel(LongAccel) -- 2.13 Firmware and up
BrakeG = getImu(0) --Prior to 2.13 Firmware
--if ReverseAccel then
BrakeG = BrakeG *-1
--BrakeG = -1.1
BrakePos = (BrakeG/MaxDecelG)*100
if BrakePos < 10 then BrakePos = 0 end
BrakePos = math.abs(BrakePos)
if BrakePos > 99 then BrakePos=100 end
setChannel(chBrake, BrakePos)
end
--10Hz update
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
updatevBrake()
end
Max RPM detection with GPIO reset
This script detects the peak RPM detected and stores it in a virtual channel. A GPIO is used to reset the channel to zero via a push button.
maxRpmId = addChannel("MaxRPM", 10)
maxRpm = 0
function rpmReset()
local rpm = getTimerRpm(0)
local clear = getGpio(0)
if rpm > maxRpm then
maxRpm = rpm
setChannel(maxRpmId, maxRpm)
end
if clear == 0 then
maxRpm = 0
setChannel(maxRpmId, maxRpm)
end
end
function onTick()
rpmReset()
end
Alerts/Notifications
Create an over-rev marker
This script will mark the datalog with an over-rev alert marker whenever RPMs are above a certain threshold. It will insert the current lap number to the OverRev channel. If multiple occurrences happen, you can take a look the event summary page and then look at each of those lap to see where and when it happened.
Given:
- RPM is connected a timer channel called RPM
- RPM over-rev condition is 8000
setTickRate(10)
overRevId = addChannel("OverRev", 10)
function onTick()
local rpm = getChannel("RPM")
if rpm ~= nil and rpm > 8000 then
setChannel(overRevId, getLapCount())
end
Create an Impact marker
This script will mark the datalog with an impact occurs (very high G-Forces). It will insert the current lap number to the Impact channel. If multiple occurrences happen, you can take a look the event summary page and then look at each of those lap to see where and when it happened.
setTickRate(10)
impactId = addChannel("Impact", 10)
function onTick()
local gsum = getChannel("Gsum")
if gsum ~= nil and gsum > 2.0 then --Assumes anything over 2.0G's is an impact. Change to suit your needs.
setChannel(impactId, getLapCount())
end
end
Control a Fan or Pump switch based on Temp
function updateDiffSwitch()
local diffTemp = getChannel("DiffTemp") --Change to your temperature channel name
if diffTemp ~=nil and diffTemp > 180 then --update temp to turn on at
setGpio(2,1)
elseif diffTemp ~=nil and diffTemp < 160 then --update temp to turn off at
setGpio(2,0) --Uses GPIO3 for output. Increase SampleRate or TickRate if it isn't turning on
end
end
Alert driver via electro-shock if oil pressure below safe threshold
This will alert driver via a shock (using pet scat mat) if oil pressure drops below threshold while engine is running above certain RPM
Script will check at 10Hz (10 times/sec) for threshold condition
Given:
- Oil pressure on analog channel 0, and calibrated
- Seat mounted pet scat mat installed in seat and controlled by GPIO 0 (GPIO switches ground when active)
- GPIO 0 is configured for output mode
- RPM is connected to timer input 0
--onTick() is called at 10Hz
setTickRate(10)
rpmThreshold = 2000
lowOilPressure = 15
function onTick()
local shockDriver = 0
if getTimerRpm(0) > rpmThreshold and getAnalog(0) < lowOilPressure then
shockDriver = 1
end
setGpio(0, shockDriver)
end
Track Max RPM / Value
This script will track a channel's maximum value and set a new channel with that maximum. Given:
- RPM is connected to the first Timer input channel
setTickRate(10)
maxRpmId = addChannel("MaxRPM", 10)
maxRpm = 0
function onTick()
local rpm = getTimerRpm(0)
if rpm > maxRpm then
maxRpm = rpm
setChannel(maxRpmId, maxRpm)
end
end
Activate a GPIO when start finish line is crossed
This script will pulse one of the GPIO outputs when the start/finish line is detected. First, the onTick rate is set to 10hz, then setGpio() is called with the result of the call to getAtStartFinish()
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
if getAtStartFinish() == 1 then
setGpio(0, 1)
else
setGpio(0, 0)
end
end
or
setTickRate(10) function onTick() setGpio(0, getAtStartFinish()) end
Temperature Warning Indicator Light
This script will activate an output if an analog input exceeds a threshold. It's assumed a temperature sensor is connected to the Analog input channel 0 and is calibrated.
More information: Installation Guide, Sensor Guide, Operation Guide
function onTick() if getAnalog(0) > 212 then setGpio(0, 1) else setGpio(0, 0) end end
Multi warning light
A script to trigger a warning light if at least one condition occurs. This will activate the output if the engine temperature is greater than 212 or if oil pressure drops below 10.
- Note Actual temperature and pressure sensors must be connected to the appropriate analog inputs and correctly calibrated.
--Analog 0 is engine temp, in degrees F --Analog 1 is oil pressure, in PSI function onTick() if getAnalog(0) > 212 or getAnalog(1) < 10 then setGpio(0, 1) else setGpio(0, 0) end end
Enable an LED if fuel level drops below 10%
- Using PWM/Analog output
only available on RaceCapture/Pro MK1 and MK2
- Fuel sensor is on Analog 0, scaled 0-100%
- LED indicator connected to PWM 0. When fuel level drops below 10%, Analog/PWM output 0 will show 5v; 0v if fuel level is higher
- PWM channel settings are set to factory default
function onTick() local p = 0 if getAnalog(0) < 10 then p = 100 end setPwmDutyCycle(0,p) end
- Using GPIO in output mode
- When fuel level drops below 10%, the GPIO is activated (output is grounded). Can be used to drive a relay or other device up to 1A load
- GPIO jumper set to output mode
- GPIO setting in firmware set to match jumper setting
function onTick() local p = 0 if getAnalog(0) < 10 then p = 1 end setGpio(0, p) end
3 stage Sequential Shift Light
Activates a 3 stage sequential shift light. Also see the Sequential Shift Light project
Given:
- RPM sensor on timer input 0
- GPIO channels are configured in output mode under Setup/GPIO
setTickRate(15) function onTick() local r = getTimerRpm(0) if r > 5000 then setGpio(2,1) else setGpio(2,0) end if r > 6000 then setGpio(1,1) else setGpio(1,0) end if r > 7000 then setGpio(0,1) else setGpio(0,0) end end
ProFormance Meter
Uses ShiftX to show you how much available grip you are using and how much is left. It also creates and updates the ProFormace channel which is an integer from 0-9. Closer to 9 you are the closer you are to max available grip.
Instead of just using GSum, this takes into account that your MaxLatG's will be different than your MaxLongG's and gives you a more accurate representation of what you can do based on whether you are braking, turning, or accelerating.
It also has 2 different models. 1) for an Advanced Driver and 2) for a Pro Driver. This is based on typical friction circles of Advanced Drivers vs Pro Drivers respectively. See the OnTick funtion to change DriverLevel.
It also has an Oversteer Alert feature for ShiftX. Change the YawThreshold value to suit your needs.
setTickRate(25)
sxSetConfig(1)
yawThreshold = 25 --At what yaw rate do you want the oversteer alarm lights to trigger' Check normal max yaw on your Podium.live race summaries to get a better idea of what value you should use
maxGsumId = addChannel("MaxGsum", 25, 2, -2.0, 2.0)
pctGsumMaxId = addChannel("PctMaxGsum", 25, 0, 0, 100)
maxLatGId = addChannel("MaxLatG", 25, 2, -2.0, 2.0)
maxBrakeGId = addChannel("MaxBrakeG", 25, 2, -2.0, 2.0)
maxAccelGId = addChannel("MaxAccelG", 25, 2, -2.0, 2.0)
ProFormanceRatingId = addChannel("ProFormance", 25, 0, 9)
maxGsum = .3
maxLatG = .2
maxBrakeG = .2
maxAccelG = .1
currLatG = 0
longG = 0
lastLongG = 0
lastLatG = 0
function updateGStats()
local gsum = getChannel("Gsum")
if gsum ~= nil and gsum > 0 then
if gsum > maxGsum then
maxGsum = gsum
setChannel(maxGsumId, maxGsum)
end
setChannel(pctGsumMaxId, (gsum / maxGsum) * 100)
end
local latG = getChannel("AccelY")
if latG ~= nil then
latG = math.abs(latG)
if latG > maxLatG then
maxLatG = latG
setChannel(maxLatGId, maxLatG)
end
end
local currLongG = getChannel("AccelX")
if currLongG ~= nil then
if currLongG>0 then
if currLongG > maxBrakeG then
maxBrakeG = currLongG
setChannel(maxBrakeGId, maxBrakeG)
end
elseif currLongG<0 then
currLongG = math.abs(currLongG)
if currLongG>maxAccelG then
maxAccelG = currLongG
setChannel(maxAccelGId, maxAccelG)
end
end
end
end
function alertYaw(Yaw) --Light up the side ShiftX lights in case of an Oversteer event
if Yaw >= yawThreshold+20 then
sxSetLed(7,2,255,255,255,9)
elseif Yaw >= yawThreshold+10 then
sxSetLed(7,2,255,255,255,5)
elseif Yaw >= yawThreshold then
sxSetLed(7,2,255,255,255,3)
else
sxSetLed(7,2,0,0,0,0)
end
end
function resetSxLeds() --resets all the ShiftX lights to off
sxSetLed(0,0,0,0,0,0)
end
function getProFormanceRating(driverLevel) --Calculate how much grip they are using and how much is left
--driverLevel: 1=Advanced, 2=Pro
local cLatG = getChannel("AccelY")
if cLatG ~= nil then currLatG = math.abs(cLatG) end
local cLongG = getChannel("AccelX")
if cLongG ~= nil then
longG = cLongG
end
local BrakeAccel = "Braking"
local maxLongG = maxBrakeG
--may not want to do this
--if longG <= -0.01 then --Calculate Accel G's seperate from Braking G's
-- BrakeAccel = "Accelerating"
-- maxLongG = maxAccelG
--end
local currLongG = math.abs(longG)
local latGAvail = 0
local longGAvail = 0
if driverLevel==1 then --Advanced driver
latGAvail = maxLatG*(1-(currLongG/maxLongG))
longGAvail = maxLongG*(1-(currLatG/maxLatG))
else --Pro Driver
latGAvail = math.sqrt(((maxLatG - ((maxLatG-maxLongG)*(currLongG/maxLongG)))^2)-(currLongG^2))
longGAvail = math.sqrt(((maxLongG - ((maxLongG-maxLatG)*(currLatG/maxLatG)))^2)-(currLatG^2))
end
local percGUsedLat
if latGAvail <= 0 then
percGUsedLat = 1
else
percGUsedLat = currLatG/latGAvail
end
local percGUsedLong
if longGAvail <= 0 then
percGUsedLong = 1
else
percGUsedLong = currLongG/longGAvail
end
local ProFormanceRating
if currLongG-lastLongG > currLatG-lastLatG then
local TotalPot2
if (math.sqrt((currLatG^2)+(longGAvail^2))) <= 0 then
TotalPot2 = 1
else
TotalPot2 = (math.sqrt((currLatG^2)+(currLongG^2)))/(math.sqrt((currLatG^2)+(longGAvail^2)))
end
local TotalPot3
if (currLatG+longGAvail) <= 0 then
TotalPot3 = 1
else
TotalPot3 = (currLatG+currLongG)/(currLatG+longGAvail)
end
local avgTotPot = (((percGUsedLat+((1-(currLatG/maxLatG))*percGUsedLong))*2)+TotalPot2+TotalPot3)/4
ProFormanceRating = math.floor(avgTotPot*10)
else
local TotalPot2
if (math.sqrt((currLongG^2)+(latGAvail^2))) <= 0 then
TotalPot2 = 1
else
TotalPot2 = (math.sqrt((currLatG^2)+(currLongG^2)))/(math.sqrt((currLongG^2)+(latGAvail^2)))
end
local TotalPot3
if (currLongG+latGAvail) <= 0 then
TotalPot3 = 1
else
TotalPot3 = (currLatG+currLongG)/(currLongG+latGAvail)
end
local avgTotPot = (((percGUsedLong+((1-(currLongG/maxLongG))*percGUsedLat))*2)+TotalPot2+TotalPot3)/4
ProFormanceRating = math.floor(avgTotPot*10)
end
if ProFormanceRating<0 then ProFormanceRating=0 end
if ProFormanceRating>9 then ProFormanceRating=9 end
setChannel(ProFormanceRatingId, ProFormanceRating)
lastLongG = currLongG
lastLatG = currLatG
return ProFormanceRating
end
function showProFormanceSx(rating) --Show ProFormanceRating on ShiftX
local numLeds=7 --How many LEDs on the ShiftX do you want to use for the ProFormance meter. Default is 7; the 7 in the middle
resetSxLeds()
sxSetLed(0,numLeds,255,0,0,0)
local percLeds = (.1*rating*(numLeds+1))
local greenLeds =math.floor(percLeds)
if greenLeds>0 then sxSetLed(0,greenLeds,0,255,0,0) end
if percLeds-greenLeds>0.61 then
sxSetLed(greenLeds,1,100,100,0,2)
end
sxSetDisplay(0,rating)
end
function onTick()
resetSxLeds()
updateGStats()
--ProFormance driver level: 1=Advanced, 2=Pro
local driverLevel = 1
local ProFormanceRating = getProFormanceRating(driverLevel)
showProFormanceSx(ProFormanceRating)--Show ProFormance Rating on ShiftX
if getChannel("Yaw")~=nil then Yaw = getChannel("Yaw") end
if math.abs(Yaw)>yawThreshold-5 then alertYaw(math.abs(Yaw)) end
collectgarbage()
end
CAN bus scripts
Receive a CAN message on one bus and re-transmit on a different bus
setTickRate(30)
function onTick()
id, ext, data = rxCAN(0)
if (id ~= nil) then
txCAN(1, id, ext, data)
end
end
Send A CAN message with current GPS speed
Given:
- Destination CAN device is looking for a message with ID 1234
- Standard (11 bit) CAN identifer
- CAN1 channel is used
function onTick()
local speed = getGpsSpeed()
--format the speed in a CAN message. Speed is in the first byte
local msg = {speed}
txCAN(0, 1234, 0, msg)
end
Send A CAN message with a temperature value
available in future Firmware version 2.0
Given:
- Analog 0 reads a calibrated temperature value between 0 and 255
- Destination CAN device is looking for a message with ID 1234
- Standard (11 bit) CAN identifer
- CAN1 channel is used
function onTick()
local tmp = getAnalog(0)
local msg = {tmp}
txCAN(0, 1234, 0, msg)
end
Use RCP as a general purpose CAN data logger
The following script will output any received CAN bus message to the log window.
- You can access the log window by enabling polling in the script window under the RaceCapture app configuration view
- You can also access the log window by connecting to RaceCapture/Pro from a terminal program (hyperterminal, Minicom, etc) and issuing the command: viewLog
setTickRate(30) --30Hz
function onTick()
repeat --will drain CAN buffer on each tick
id, e, data = rxCAN(0)
if id ~= nil then
print(id ..':')
for i=1,#data do
print(data[i] ..' ')
end
println('')
end
until id == nil
end
Receive a CAN message and set a virtual channel
Given:
- creates a channel named "MyChannel" that logs at 10Hz
- Sets tick rate to 10Hz
- Receive a CAN message on CAN1 channel, with 100ms timeout
- if data received is valid (by checking the CAN message ID is not nil), then set the virtual channel with the first element in the CAN message data
channelId = addChannel("MyChannel", 10)
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
id, ext, data = rxCAN(0, 100)
if id ~= nil then
setChannel(channelId, data[1])
end
end
Note: To map real CAN bus data, consult your CAN bus protocol documentation for correctly mapping CAN bus data to virtual channels.
CAN bus loopback test
Use This script to test functionality of your CAN bus.
Wiring / Setup
- Connect CAN1 high -> CAN2 high and CAN1 low -> CAN2 low. This can either be done though the main wiring harness or the RJ45 connector.
- Note if your unit has CAN on the wiring harness and the RJ45 connector, you only need to bridge the connections on one harness, since they are internally wired together.
- Set the CAN baud rates to the same value for CAN1 and CAN 2.
-- CAN loopback test
-- * Wire CAN1 high -> CAN2 high and CAN 1 low -> CAN 2 low
-- * Ensure baud rate is identical for both CAN1 and CAN2
can_id = 1234
count = 0
function onTick()
count = count + 1
-- transmit a CAN message on CAN1 with count as the first byte
local tx_result = txCAN(0, can_id, 0, {count})
println('transmit result ' ..tx_result)
-- receive a CAN message on CAN2
local id, ext, data = rxCAN(1)
if id == nil then
println('No CAN message received!')
else
println('Got CAN message ID: ' ..id ..' data: ' ..data[1])
end
end
Serial Port
Read an analog sensor value and output it to the auxiliary serial port
This example reads an analog sensor and writes a string containing the value to the Auxiliary serial port. Repeats once per second.
--initialize Aux serial port to 115200, 8, N, 1 initSer(4, 115200, 8, 0, 1) function onTick() value = getAnalog(0) writeSer(4, 'A=' ..value) end
Read a line of serial data
This example reads a line of serial data and writes it to the internal RaceCapture log.
- Note: You can monitor the log by enabling the log polling in the script configuration view.
--initialize Aux serial port to 115200, 8, N, 1
initSer(4, 115200, 8, 0, 1)
function onTick()
--read a line from the aux serial port with a 100ms timeout
value = readSer(4, 100)
if value ~= nil then
println('read value: ' ..value)
end
end
Demo Scripts
RPM Sweep
This sweeps an RPM channel up and down through a pre-defined range. Edit the range at the top of the script.
-- 05 Jan 2016 RPM demo
-- F.Mirandola - B.Picasso
-- This code will show a demo RPM sweep on RaceCapturePro
thrRpmLo = 3000
--Low RPM threshold for change direction
thrRpmHi = 10000
--Hi RPM threshold for change direction
incrementRpm = 300
--Step between each RPM increment/decrement, will affect the speed, higher = faster
-- Do not edit after this!!
setTickRate(10)
rpm = 0
direction = 0
rpmId = addChannel("RPM", 10, 0, 0, 10000)
function onTick()
setChannel(rpmId, rpm)
if (rpm<=thrRpmHi and direction == 0 ) then rpm = rpm + incrementRpm
elseif (rpm>=thrRpmLo and direction == 1 ) then rpm = rpm - incrementRpm
end
if (rpm>thrRpmHi) then direction = 1
elseif (rpm<thrRpmLo) then direction = 0
end
end
Simulating Laps
Here's a neat script that can simulate lap times and predicted times. We've used it to develop dashboard features for the app. Especially interesting is the use of the accelerometer to generate a bit of noise and variability in the data.
--Script to simulate lap and predicted times
--Without needing a moving car on race track!
--To use, disable Race Timing in RaceCapture/Pro configuration and
--use this script
etid = addChannel("ElapsedTime", 10, 4)
ltid = addChannel("LapTime", 10, 4)
ptid = addChannel("PredTime", 10, 4)
clid = addChannel("CurrentLap", 10, 0)
lcid = addChannel("LapCount", 10, 0)
et = 0 --ElapsedTime value
lt = 0 --LapTime value
pt = 0 --PredTime value
cl = 0 --CurrentLap value
lc = 0 --LapCount value
targetTime = 0.5 --target time for our fake laps
setTickRate(10)
function onTick()
local rnd = getImu(0) --use the IMU to create a random-ish number
--simulate a predicted time if we've already
--completed a lap
--rnd value makes the predicted time jiggle
if lc > 0 then
pt = targetTime + rnd
setChannel(ptid, pt)
end
--increment elapsed time by 1/10 second
et = et + 0.00166666667
setChannel(etid, et)
if et > targetTime + rnd then
lt = et
setChannel(ltid, lt)
et = 0
cl = cl + 1
setChannel(clid, cl)
if cl > 1 then
lc = lc + 1
setChannel(lcid, lc)
end
end
end